Path integral formulation
The path integral formulation, here from the statistical mechanical point of view, is an elegant method by which quantum mechanical contributions can be incorporated within a classical simulation using Feynman path integrals (see the additional reading section). Such simulations are particularly applicable to light atoms and molecules such as hydrogen, helium, neon and argon, as well as quantum rotators such as methane and hydrogen-bonded systems such as water. From a more idealised point of view path integrals are often used to study quantum hard spheres.
Principles
In the path integral formulation the canonical partition function (in one dimension) is written as ([1] Eq. 1)
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Q(\beta, V)= \int {\mathrm d} x_1 \int_{x_1}^{x_1} Dx(\tau)e^{-S[x(\tau)]}}
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S[x(\tau)]} is the Euclidean action, given by ([1] Eq. 2)
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S[x(\tau)] = \int_0^{\beta \hbar} H(x(\tau)) ~{\mathrm d}\tau}
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x(\tau)} is the path in time Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tau} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle H} is the Hamiltonian. This leads to ([1] Eq. 3)
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Q_P = \left( \frac{mP}{2 \pi \beta \hbar^2} \right)^{P/2} \int ... \int {\mathrm d}x_1... {\mathrm d}x_P e^{-\beta \Phi_P (x_1...x_P;\beta)}}
where the Euclidean time is discretised in units of
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \varepsilon = \frac{\beta \hbar}{P}, P \in {\mathbb Z}}
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x_t = x(t \beta \hbar/P)}
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x_{P+1}=x_1}
and ([1] Eq. 4)
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Phi_P (x_1...x_P;\beta)= \frac{mP}{2\beta^2 \hbar^2} \sum_{t=1}^P (x_t - x_{t+1})^2 + \frac{1}{P} \sum_{t=1}^P V(x_t)}
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle P} is the Trotter number. In the Trotter limit, where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle P \rightarrow \infty} these equations become exact. In the case where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle P=1} these equations revert to a classical simulation. It has long been recognised that there is an isomorphism between this discretised quantum mechanical description, and the classical statistical mechanics of polyatomic fluids, in particular flexible ring molecules[2], due to the periodic boundary conditions in imaginary time. It can be seen from the first term of the above equation that each particle Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x_t} interacts with is neighbours Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x_{t-1}} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x_{t+1}} via a harmonic spring. The second term provides the internal potential energy.
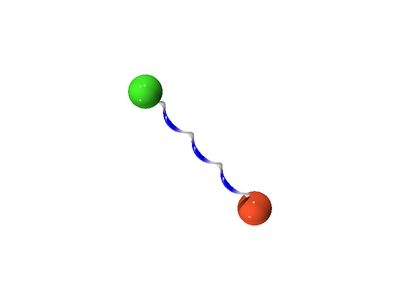
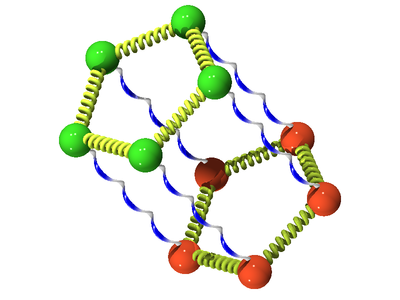
The following is a schematic for the interaction between atom Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle i} (green) and atom Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle j} (orange). Here we show the atoms having five Trotter slices (Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle P=5} ), forming what can be thought of as a "ring polymer molecule". The harmonic springs between Trotter slices are in yellow, and white/blue bonds represent the classical intermolecular pair potential.
In three dimensions one has the density operator
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{\rho} (\beta) = \exp\left[ -\beta \hat{H} \right]}
which thanks to the Trotter formula we can tease out Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \exp \left[ -\beta (U_{\mathrm {spring}}+ U_{\mathrm{internal}} ) \right]} , where
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle U_{\mathrm {spring}} = \frac{mP}{2\beta^2 \hbar^2} \sum_{t=1}^P | \mathbf{r}_t - \mathbf{r}_{t+1} |^2}
and
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle U_{\mathrm{internal}}= \frac{1}{P} \sum_{t=1}^P V(\mathbf{r}_t)}
The internal energy is given by
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle U \rangle = \frac{3NP}{2\beta}- \langle U_{\mathrm {spring}} \rangle + \langle U_{\mathrm{internal}} \rangle }
The average kinetic energy is known as the primitive estimator, i.e.
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle K_P \rangle = \frac{3NP}{2\beta}- \langle U_{\mathrm {spring}} \rangle }
Harmonic oscillator
The density matrix for a harmonic oscillator is given by ([3] Eq. 10-44)
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \rho(x',x)= \sqrt{ \frac{m \omega}{2 \pi \hbar \sinh \omega \beta \hbar} } \exp \left( - \frac{m \omega}{2 \hbar (\sinh \omega \beta \hbar)^2 } \left( (x^2 + x'^2 ) \cosh \omega \beta \hbar - 2xx'\right)\right)}
Wick rotation and imaginary time
Wick rotation [6]. One can identify the inverse temperature, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \beta} with an imaginary time Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle it/\hbar} (see [7] § 2.4).
Rotational degrees of freedom
In the case of systems having (Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle d} ) rotational degrees of freedom the Hamiltonian can be written in the form ([8] Eq. 2.1):
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{H} = \hat{T}^{\mathrm {translational}} + \hat{T}^{\mathrm {rotational}}+ \hat{V}}
where the rotational part of the kinetic energy operator is given by ([8] Eq. 2.2)
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T^{\mathrm {rotational}} = \sum_{i=1}^{d^{\mathrm {rotational}}} \frac{\hat{L}_i^2}{2\Theta_{ii}}}
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{L}_i} are the components of the angular momentum operator, and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Theta_{ii}} are the moments of inertia.
Rigid rotators
- Main article: Rigid top propagator
Computer simulation techniques
The following are a number of commonly used computer simulation techniques that make use of the path integral formulation applied to phases of condensed matter
Path integral Monte Carlo
Path integral Monte Carlo (PIMC) [9]
Path integral molecular dynamics
Path integral molecular dynamics (PIMD) [10]
Centroid molecular dynamics
Centroid molecular dynamics (CMD) [11] [12] [13] [14] [15]
Ring polymer molecular dynamics
Ring polymer molecular dynamics (RPMD) [16] [17] (Contraction scheme [18] [19])
Normal mode PIMD
Grand canonical Monte Carlo
A path integral version of the Widom test-particle method for grand canonical Monte Carlo simulations: [20]
Applications
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 B. J. Berne and D. Thirumalai "On the Simulation of Quantum Systems: Path Integral Methods", Annual Review of Physical Chemistry 37 pp. 401-424 (1986)
- ↑ David Chandler and Peter G. Wolynes "Exploiting the isomorphism between quantum theory and classical statistical mechanics of polyatomic fluids", Journal of Chemical Physics 74 pp. 4078-4095 (1981)
- ↑ R. P. Feynman and A. R. Hibbs "Path-integrals and Quantum Mechanics", McGraw-Hill, New York (1965) ISBN 0-07-020650-3
- ↑ Barry R. Holstein "The harmonic oscillator propagator", American Journal of Physics 66 pp. 583-589 (1998)
- ↑ L. Moriconi "An elementary derivation of the harmonic oscillator propagator", American Journal of Physics 72 pp. 1258-1259 (2004)
- ↑ G. C. Wick "Properties of Bethe-Salpeter Wave Functions", Physical Review 96 pp. 1124-1134 (1954)
- ↑ M. J. Gillan "The path-integral simulation of quantum systems" in "Computer Modelling of Fluids Polymers and Solids" eds. C. R. A. Catlow, S. C. Parker and M. P. Allen, NATO ASI Series C 293 pp. 155-188 (1990) ISBN 978-0-7923-0549-1
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Dominik Marx and Martin H Müser "Path integral simulations of rotors: theory and applications", Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter 11 pp. R117-R155 (1999)
- ↑ J. A. Barker "A quantum-statistical Monte Carlo method; path integrals with boundary conditions", Journal of Chemical Physics 70 pp. 2914- (1979)
- ↑ M. Parrinello and A. Rahman "Study of an F center in molten KCl", Journal of Chemical Physics 80 pp. 860- (1984)
- ↑ Jianshu Cao and Gregory A. Voth "The formulation of quantum statistical mechanics based on the Feynman path centroid density. I. Equilibrium properties", Journal of Chemical Physics 100 pp. 5093-5105 (1994)
- ↑ Jianshu Cao and Gregory A. Voth "The formulation of quantum statistical mechanics based on the Feynman path centroid density. II. Dynamical properties", Journal of Chemical Physics 100 pp. 5106- (1994)
- ↑ Seogjoo Jang and Gregory A. Voth "A derivation of centroid molecular dynamics and other approximate time evolution methods for path integral centroid variables", Journal of Chemical Physics 111 pp. 2371- (1999)
- ↑ Rafael Ramírez and Telesforo López-Ciudad "The Schrödinger formulation of the Feynman path centroid density", Journal of Chemical Physics 111 pp. 3339-3348 (1999)
- ↑ E. A. Polyakov, A. P. Lyubartsev, and P. N. Vorontsov-Velyaminov "Centroid molecular dynamics: Comparison with exact results for model systems", Journal of Chemical Physics 133 194103 (2010)
- ↑ Ian R. Craig and David E. Manolopoulos "Quantum statistics and classical mechanics: Real time correlation functions from ring polymer molecular dynamics", Journal of Chemical Physics 121 pp. 3368- (2004)
- ↑ Bastiaan J. Braams and David E. Manolopoulos "On the short-time limit of ring polymer molecular dynamics", Journal of Chemical Physics 125 124105 (2006)
- ↑ Thomas E. Markland and David E. Manolopoulos "An efficient ring polymer contraction scheme for imaginary time path integral simulations", Journal of Chemical Physics 129 024105 (2008)
- ↑ Thomas E. Markland and David E. Manolopoulos "A refined ring polymer contraction scheme for systems with electrostatic interactions" Chemical Physics Letters 464 pp. 256-261 (2008)
- ↑ Qinyu Wang, J. Karl Johnson and Jeremy Q. Broughton "Path integral grand canonical Monte Carlo", Journal of Chemical Physics 107 pp. 5108-5117 (1997)
- ↑ Jianshu Cao and Gregory A. Voth "Semiclassical approximations to quantum dynamical time correlation functions", Journal of Chemical Physics 104 pp. 273-285 (1996)
- ↑ C. Chakravarty and R. M. Lynden-Bell "Landau free energy curves for melting of quantum solids", Journal of Chemical Physics 113 pp. 9239-9247 (2000)
Additional reading
- P. A. M. Dirac "The Lagrangian in Quantum Mechanics", Physikalische Zeitschrift der Sowjetunion 3 pp. 64-72 (1933)
- R. P. Feynman "Statistical Mechanics", Benjamin, Reading, Massachusetts, (1972) ISBN 0-201-36076-4 Chapter 3.
- Tohru Morita "Solution of the Bloch Equation for Many-Particle Systems in Terms of the Path Integral", Journal of the Physical Society of Japan 35 pp. 980-984 (1973)
- F. W. Wiegel "Path integral methods in statistical mechanics", Physics Reports 16 pp. 57-114 (1975)
- J. A. Barker "A quantum-statistical Monte Carlo method; path integrals with boundary conditions", Journal of Chemical Physics 70 pp. 2914-2918 (1979)
- D. M. Ceperley "Path integrals in the theory of condensed helium", Reviews of Modern Physics 67 279 - 355 (1995)
- Charusita Chakravarty "Path integral simulations of atomic and molecular systems", International Reviews in Physical Chemistry 16 pp. 421-444 (1997)
- Jean Zinn-Justin "Path integral" Scholarpedia, 4(2):8674 (2009)
External links
- Density matrices and path integrals computer code on SMAC-wiki.
- A simple implementation of PIMD integrator (C++).