Hard superball model
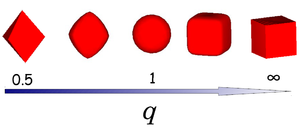
The hard superball model is defined by the inequality
where x, y and z are scaled Cartesian coordinates with q the deformation parameter and radius a. The shape of the superball interpolates smoothly between two Platonic solids, namely the octahedron (q = 0.5) and the cube (q = ∞) via the sphere (q = 1) as shown in the right figure.
Particle Volume
The volume of a superball with the shape parameter q and radius a is given by
- Failed to parse (Conversion error. Server ("https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_") reported: "Cannot get mml. Server problem."): {\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}v(q,a)&=&8a^{3}\int _{0}^{1}\int _{0}^{(1-x^{2q})^{1/2q}}(1-x^{2q}-y^{2q})^{1/2q}\mathrm {d} \,y\,\mathrm {d} \,x={\frac {2a^{3}\left[\Gamma \left(1/2q\right)\right]^{3}}{3q^{2}\Gamma \left(3/2q\right)}},\end{aligned}}}
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Gamma} is the Gamma function.
Overlap algorithm
The most widely used overlap algorithm is on the basis of Perram and Wertheim method [1] [2].
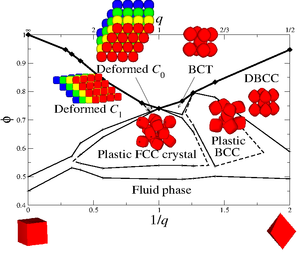
Phase diagram
The full phase diagram of hard superballs whose shape interpolates from cubes to octahedra was reported in Ref [2].
References
- ↑ John W. Perram and M. S. Wertheim "Statistical mechanics of hard ellipsoids. I. Overlap algorithm and the contact function", Journal of Computational Physics 58 pp. 409-416 (1985)
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 R. Ni, A.P. Gantapara, J. de Graaf, R. van Roij, and M. Dijkstra "Phase diagram of colloidal hard superballs: from cubes via spheres to octahedra", Soft Matter 8 pp. 8826-8834 (2012)

