Hard superball model
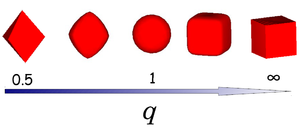
A superball is defined by the inequality
- Failed to parse (Conversion error. Server ("https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_") reported: "Cannot get mml. Server problem."): {\displaystyle {\frac {x^{2}}{a^{2q}}}+{\frac {y^{2}}{a^{2q}}}+{\frac {z^{2}}{a^{2q}}}\leq 1}
where x, y and z are scaled Cartesian coordinates with q the deformation parameter, and we use radius a of the particle as our unit of length. The shape of the superball interpolates smoothly between two Platonic solids, namely the octahedron (q = 0.5) and the cube (q = ∞) via the sphere (q = 1) as shown in the left figure.