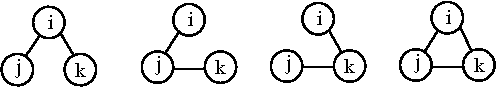Cluster integrals: Difference between revisions
Carl McBride (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Carl McBride (talk | contribs) m (→References: Added a reference.) |
||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
# Joseph Edward Mayer and Maria Goeppert Mayer "Statistical Mechanics" John Wiley and Sons (1940) Chapter 13. | # Joseph Edward Mayer and Maria Goeppert Mayer "Statistical Mechanics" John Wiley and Sons (1940) Chapter 13. | ||
#[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0003-4916(58)90058-7 Edwin E. Salpeter "On Mayer's theory of cluster expansions", Annals of Physics '''5''' pp. 183-223 (1958)] | |||
[[Category: Statistical mechanics]] | [[Category: Statistical mechanics]] | ||
Revision as of 13:37, 28 April 2008
In an ideal gas there are no intermolecular interactions. However, in an imperfect or real gas, this is not so, and the second virial coefficient is other than zero. Mayer and Mayer developed a theoretical treatment of the virial coefficients in terms of cluster integrals.
The simplest cluster is that consisting of a single molecule, not bound to any other. A cluster of three specified identical molecules, i, j and k may be formed in any of four ways:
The first three cluster integrals are (Ref. 1 Eq. 13.6)
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle b_1 = \frac{1}{1!V}\int d\tau_1 =1}
Ref. 1 Eq. 13.7:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle b_2 = \frac{1}{2!V} \iint f(r_{12}) d\tau_2 d\tau_1 = \frac{1}{2}\int_0^\infty 4\pi r^2 f(r) dr}
and Ref. 1 Eq. 13.8:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle b_3 = \frac{1}{3!V} \iiint (f_{31} f_{21} + f_{32}f_{31} + f_{32}f_{21} + f_{32}f_{31}f_{21}) d\tau_3 d\tau_2 d\tau_1}
using the Mayer f-function notation.
Irreducible clusters
Irreducible clusters are denoted by Failed to parse (Conversion error. Server ("https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_") reported: "Cannot get mml. Server problem."): {\displaystyle \beta _{k}}
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \beta_1 = \int f_{31} d\tau_3 = \frac{1}{V}\iint f_{12}d\tau_1 d\tau_2 =\int_0^\infty 4 \pi r^2 f(r) dr}
note Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle b_2 = \frac{1}{2}\beta_1} .
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \beta_2 = \frac{1}{2V}\iiint f_{32}f_{31}f_{21} d\tau_1 d\tau_2 d\tau_3 }
note Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle b_3 = \frac{1}{2} \beta_1^2 + \frac{1}{3}\beta_2}
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \beta_3 = \frac{1}{6V}\iiiint (3f_{43}f_{32}f_{21}f_{41}+6f_{43}f_{32}f_{21}f_{41}f_{31} + f_{43}f_{32}f_{21}f_{41}f_{31}f_{42})d\tau_1 d\tau_2 d\tau_3 d\tau_4 }
note Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle b_4 = \frac{2}{3}\beta_1^3 + \beta_1 \beta_2 + \frac{1}{4}\beta_3}
See also
References
- Joseph Edward Mayer and Maria Goeppert Mayer "Statistical Mechanics" John Wiley and Sons (1940) Chapter 13.
- Edwin E. Salpeter "On Mayer's theory of cluster expansions", Annals of Physics 5 pp. 183-223 (1958)