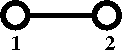Mayer f-function: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Carl McBride (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Carl McBride (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The '''Mayer ''f''-function''', or ''f-bond'' is defined as: | |||
:<math>f_{ | :<math>f_{12}=f(r_{12})= \exp\left(-\frac{\Phi_{12}(r)}{k_BT}\right) -1 </math> | ||
where | where | ||
* <math>k_B</math> is the [[Boltzmann constant]] | * <math>k_B</math> is the [[Boltzmann constant]]. | ||
* <math>T</math> is the temperature | * <math>T</math> is the [[temperature]]. | ||
* <math> | * <math>\Phi_{12}(r)</math> is the [[intermolecular pair potential]]. | ||
Diagrammatically the Mayer ''f''-function is written as | |||
[[Image:Mayer_f_function.png]] | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
#[http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.1723631 Joseph E. Mayer "Contribution to Statistical Mechanics", Journal of Chemical Physics '''10''' pp. 629-643 (1942)] | |||
[[Category: Statistical mechanics]] | [[Category: Statistical mechanics]] | ||
[[Category: Integral equations]] | [[Category: Integral equations]] | ||
Revision as of 14:27, 25 June 2007
The Mayer f-function, or f-bond is defined as:
where
- is the Boltzmann constant.
- is the temperature.
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Phi_{12}(r)} is the intermolecular pair potential.
Diagrammatically the Mayer f-function is written as