SPC model of water: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (Changed internal link.) |
m (Added a section on the surface tension) |
||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
The SPC model has a [[dipole moment]] of 2.27 D. | The SPC model has a [[dipole moment]] of 2.27 D. | ||
==Surface tension== | |||
The [[surface tension]] has been studied for the SPC model by Vega and Miguel. | |||
*[http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.2715577 C. Vega and E. de Miguel "Surface tension of the most popular models of water by using the test-area simulation method", Journal of Chemical Physics '''126''' 154707 (2007)] | |||
==Related models== | ==Related models== | ||
Over the years a number of variants of the SPC model have been published: | Over the years a number of variants of the SPC model have been published: | ||
*[[SPC]] | |||
*[[SPC/E]] | *[[SPC/E]] | ||
*[[SPC/F]] | *[[SPC/F]] | ||
Revision as of 15:30, 2 July 2009
The simple point charge (SPC) model [1] is an empirical model of water. The molecule is modelled as a rigid isosceles triangle, having charges situated on each of the three atoms. Apart from Coulombic interactions, the molecules interact via long-range Lennard-Jones sites, situated on the oxygen atoms. The parameters are as follows:
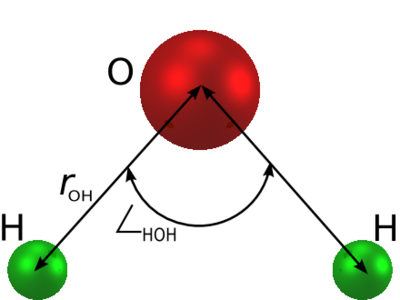
| parameter | value |
| Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \sigma} | Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 3.166 {\mathrm {\AA}}} |
| Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \epsilon} | Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 0.650} kJ mol-1 |
| Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 1.000\mathrm{\AA}} | |
| Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \angle_\mathrm{HOH}} | Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 109.47^{\circ}} |
| Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle q_{\mathrm{O}}} | |
| Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle q_{\mathrm{H}}} | Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle q_{\mathrm{O}}/2} (charge neutrality) |
The SPC model has a dipole moment of 2.27 D.
Surface tension
The surface tension has been studied for the SPC model by Vega and Miguel.
Related models
Over the years a number of variants of the SPC model have been published:
References
- ↑ H. J. C. Berendsen, J. P. M. Postma, W. F. van Gunsteren and J. Hermans, in: Intermolecular Forces (B. Pullman, ed.), Reidel, Dordrecht, p. 331 (1981)

